Facts about 5G and the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic Spectrum and the 5G frequencies
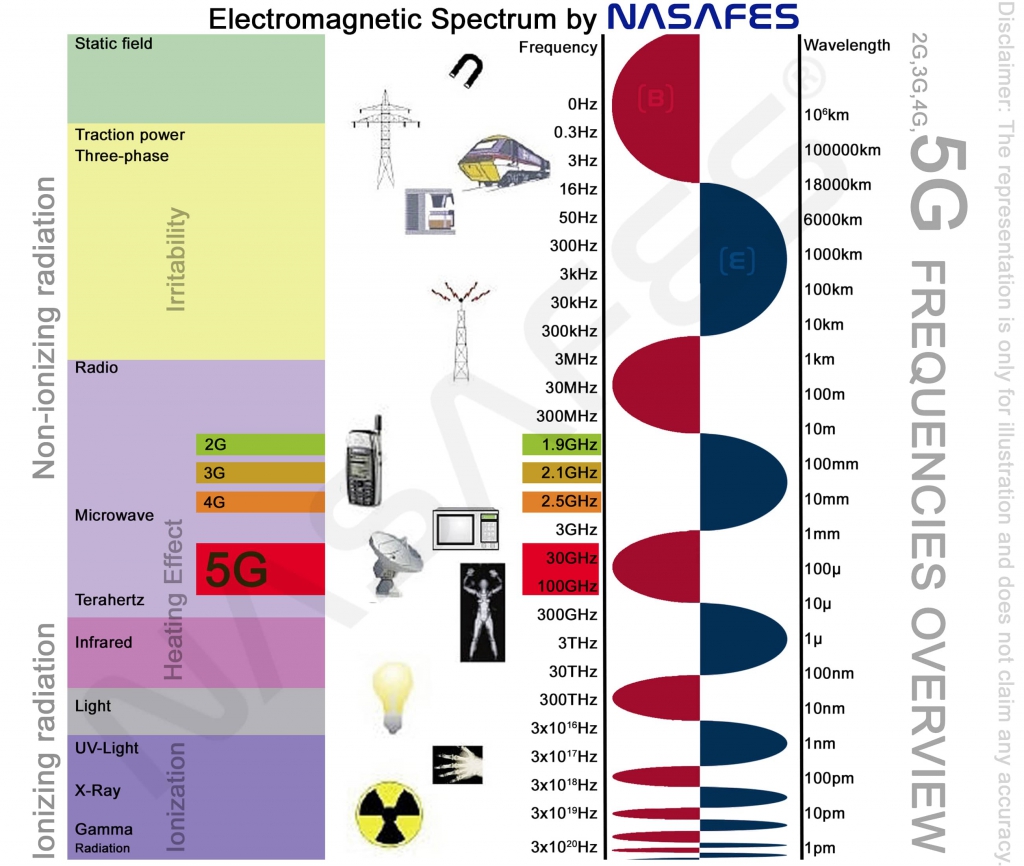
The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the frequencies and wavelengths that encompass electromagnetic radiation, which is the flow of energy at the speed of light through free space or a vacuum in the form of electric or magnetic fields. Some good examples of electromagnetic radiation include radio waves, gamma rays, visible light and also 5g radiation. Characteristic of these waves are their frequency and intensity and each has it’s own identifiable pattern. Encompassing all of these variations, the electromagnetic spectrum is made up of several subranges, more commonly known as portions. Each portion represents a different set of characteristics and behaviors based on the emission, transmission, absorption, and application of the various waves.
Frequency and Wavelength of 5G and electromagnetic spectrum
Frequency is defined as the number of times a wave passes a particular point within a unit of time. Wavelength on the other hand is characterized by the distance between two corresponding points of two waves. Both of these measurements play a part in determining where a particular type of energy or wave falls on the electromagnetic spectrum. For example, radio waves are less intense an are on the low frequency end of the spectrum with long wavelengths, while gamma rays are more intense with high frequencies and shorter wavelengths. Visible light falls on the middle of this scale and is responsible for making it possible for things to be seen by the human eye. Between the microwaves and the terahertz waves creates a significant heat effect. Coincidentally, 5G radiation (see the red bar) falls directly in this radiation area.
Generation of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation occurs whenever a charged particle, such as electrons or protons, change direction suddenly. This happens whenever the particle increases or decreases speed. Ultimately, the change causes the particle to discharge energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. A prime example of this occurring is via radio waves emitted from a radio antenna. The charges released from an antenna are considered to be oscillating and can be set to oscillate at a set frequency. The ability to emit at this set frequency also opens up the ability to absorb at the same frequency.
The generation of electromagnetic radiation is separated into two categories. The first includes systems that produce electromagnetic radiation at a broad spectrum of frequencies and the second includes those that emit and absorb at discrete frequencies from certain systems. The sun is a great example of the first system since the energy and radiation from the sun is produced on broad and consistent level. On the other hand, the radio antenna from the earlier section is a good example of the second since it is an oscillating or looped system.